科學依據
科學數據格線軟體的主要目標是建立科學資料庫的統一安全體系,實現科學資料庫分散式、異構資源的統一訪問接口,由SDG中間件和SDG工具集構成。信息服務存儲數據服務所需的核心目錄信息,為數據訪問服務提供目錄服務;數據訪問服務是SDG中間件的核心部分,它建立在由安全體系構建的安全環境下,對外提供統一的數據訪問接口,禁止分散式環境中數據資源的多樣性和異構性,消除數據孤島和信息孤島,實現科學資料庫數據資源的集成與共享;存儲服務為各建庫單位提供數據存儲、備份和網路服務;安全服務為SDG軟體中其它模組提供認證和授權信息,確保數據訪問的安全性。
核心服務
SDG中間件的核心服務模組包括四個子系統。信息服務子系統是為格線中的數據資源提供統一的信息服務,包括數據資源的屬性信息、狀態信息和特有的元數據信息等,實現資源描述和資源發現等功能。數據訪問服務子系統是為大規模、分布、自治、異構的數據資源提供統一的訪問接口,以方便科學資料庫數據資源的共享和集成。存儲服務子系統提供具有數據傳輸、存儲管理以及配額分配功能的存儲服務,利用高速網路環境提供網路服務,從而更有效利用數據中心的海量存儲資源,解決各建庫單位數據存儲、備份和開展網路服務的困難。安全體系子系統提供科學數據格線中的統一安全體系和相應服務,包括訪問數據資源所需的單點登錄、認證、訪問控制和記賬服務,實現對數據資源有控制、有保障、有效率的共享。
SDG中間件的套用服務模組是SDG中間件的基礎上提供了一些管理和套用工具。包括數據量統計分析工具、通用元數據管理工具、科學資料庫CA系統、格線門戶、通用數據管理工具、數據目錄管理工具、訪問控制工具包和存儲共享工具等
發展歷史
四百年前伽利略首次把望遠鏡指向天空,結束了人類一直用肉眼進行天文觀測的歷史。一百五十年前,照相技術和光譜技術開始在天文觀測中套用,單純以人眼作為天文探測器的時代結束,天體物理學誕生並發展成為現代天文學的主流。五十多年前,在第二次世界大戰中得到蓬勃發展的無線電技術使得天文學家的視野超出了可見光,射電天文學誕生。此後不久宇航時代到來,空間天文學誕生,人類對宇宙的觀測擴展到了伽馬射線、X射線、紫外和紅外波段。
從二十世紀九十年代開始,天文學正經歷著革命性的變化。這一變化是由前所未有的技術進步推動的,即望遠鏡的設計和製造、大尺寸探測器陣列的開發、計算能力的指數增長以及網際網路的飛速發展。
望遠鏡技術的進步使得人類可以建造大型的空間天文台,為伽瑪射線、X射線、光學和紅外天文的發展開闢了新的前景,同時也推動了新一代的大口徑地面光學望遠鏡和射電望遠鏡的建造,天文學家們正在計畫建造功能更好口徑更大的空間和地面望遠鏡,並將配備尺寸更大象素更多的探測器。隨著眾多先進的地面與空間天文設備的投入使用,大規模的觀測數據正在產生,例如目前哈勃空間望遠鏡每天大約產生50億位元組的數據,我國正在建造的LAMOST望遠鏡也將產生每天30億位元組的數據,美國計畫建造的“大口徑巡天望遠鏡”將會達到每天10萬億位元組的量級!目前,世界天文學數據量增倍的周期已經縮短到一年以內。
使天文學研究發生重大變化的另一個技術進步是快速網際網路技術,這使得異地天文數據的交換和處理成為可能,使得觀測數據具有巨大的科學產出的潛在意義。
天文觀測
巡天,就是對整個天區進行觀測、普查。如果利用伽馬射線巡天、X射線巡天、紫外巡天、光學巡天、紅外巡天和射電巡天所得到的觀測數據,用適合的方法對數據進行統一規範的整理、歸檔,便可以構成一個全波段的數字虛擬天空;而根據用戶要求獲得某個天區的各類數據,就仿佛是在使用一架虛擬的天文望遠鏡;如果再根據科學研究的要求開發出功能強大的計算工具、統計分析工具和數據挖掘工具,這就相當於擁有了虛擬的各種研究設施。這樣,由數字虛擬天空、虛擬天文望遠鏡和虛擬研究設施所組成的機構便是一個獨一無二的虛擬天文台。
中醫理論
中醫藥虛擬研究院由全國20餘家中醫藥大學、學院及研究院所的近300位中醫藥資料庫建設工作者組成。包括:中國中醫研究院中醫藥信息研究所、中國中醫研究院醫史文獻研究所、上海中醫藥大學、成都中醫藥大學、廣州中醫藥大學、北京中醫藥大學、黑龍江中醫藥大學、南京中醫藥大學、山東中醫藥大學、福建中醫學院、湖北中醫學院、遼寧中醫學院、河南中醫學院、山西中醫學院、天津中醫學院、陝西省中醫藥研究院、吉林省中醫藥研究院、江西省中醫藥研究院、河南省中醫藥研究院、浙江省中醫藥研究院、上海市中醫藥文獻館、重慶中藥研究院、重慶中醫研究院等單位。通過集成已開發的70多箇中醫藥資料庫,建立一個虛擬的支持中醫藥科學研究的套用格線環境,建設中醫藥虛擬研究院。
高能物理的研究與信息技術密切相關,無論是大規模實驗數據的處理,還是科學計算,以及貴重設備的共享,都可以是格線技術的直接套用。事實上,格線的發展在很大程度上就是得益於高能物理研究的推動。目前,國際上有幾個重要的格線項目都與高能物理有直接的關係,如EU DataGrid、GriPhyN、PPDG、GridPP、等等。因此,高能物理格線是一類最有代表性的格線套用。甚至可以說,格線計算將是近期解決高能物理實驗這樣的世界性合作的、數據量極大的科學工程計算問題的唯一途徑。
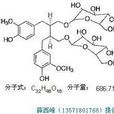
2.亞麻木酚素 (SDG)
亞麻木酚素的英文名: Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside;SDG;
2,3-Bis(3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzyl)butane-1,4-diol 1,4-diglucoside
亞麻木酚素的分子式: C32H46O16 亞麻木酚素的分子量: 686.71
亞麻木酚素的CAS No.: 148244-82-0
別名:亞麻木酯素,亞麻木脂素
純度: 95%, 98%, 99% by HPLC
詳細介紹
物品介紹
亞麻木酚素叫開環異落葉松酚二葡萄糖苷。這是與人體雌激素十分相似的植物雌激素。亞麻木酚素主要存在於亞麻籽中,其含量取決於亞麻品種、氣候和生態條件,一般約占籽重量的0.9%~1.5%,比其它已知含木酚素的66種食品高100~800倍.
來源
為亞麻科植物亞麻Linum usitatissimum L.的種子。
性狀
黃褐色粉末。
功能作用
亞麻木酚素對雌激素依賴性疾病乳腺癌、前列腺癌、經期綜合徵、骨質疏鬆有預防作用。除此之外,臨床研究顯示亞麻木酚素對糖尿病、胃腸腫瘤、冠心病、腎臟病,抗氧化性都有有益的作用。
套用狀況
近年來,以加拿大、澳大利亞、英國和美國為主的西方已開發國家,對亞麻籽作為功能食品的研究和開發作了大量的工作,以亞麻籽粉為代表的產品早已面市多年,成為中、老年人的常備保健品。最近,符合療效性要求的高純度、標準化木酚素提取物的產品也上市,可以廣泛套用於膠囊、壓片、穀物早餐和快餐食品的添加劑。還有含有ω-3脂肪酸、可溶性食物纖維和木酚素的營養功能性超濃乳狀液和全乳飲料等多種產品不斷出現在市場上。我國近幾年一些工廠也開始研究亞麻木酚素的提取工作。
Lignans are naturally occurring chemicals widespread within the plant and animal kingdoms. Several lignans—with intimidating names such as secoisolariciresinol—are considered to be phytoestrogens, plant chemicals that mimic the hormone estrogen. These are especially abundant in flaxseeds and sesame seeds. Bacteria in our intestines convert the naturally occurring phytoestrogens from flaxseed into two other lignans, enterolactone and enterodiol, which also have estrogen-like effects. In this article, the term lignans refers to these two specific lignans as well as the phytoestrogen kind, but not to the wide variety of other lignans.
Lignans are being studied for possible use in cancer prevention, particularly breast cancer. Like other phytoestrogens (such as soy isoflavones), they hook onto the same spots on cells where estrogen attaches. If there is little estrogen in the body (after menopause, for example), lignans may act like weak estrogen; but when natural estrogen is abundant in the body, lignans may instead reduce estrogen's effects by displacing it from cells. This displacement of the hormone may help prevent those cancers, such as breast cancer, that depend on estrogen to start and develop. In addition, at least one test tube study suggests that lignans may help prevent cancer in ways that are unrelated to estrogen.1
Requirements/Sources
The richest source of lignans is flaxseed (sometimes called linseed), containing more than 100 times the amount found in other foods! 11 Flaxseed oil, however, does not contain appreciable amounts of lignans.12 Sesame seed is an equally rich source.44 Other food sources are pumpkin seeds, whole grains, cranberries, and black or green tea.13
Therapeutic Dosages
Effective dosages of purified lignans have not been determined. In studies of flaxseed as a source of lignans, flaxseed has been taken at a dose of 5 to 38 g daily.
Cooking flaxseed apparently does not decrease the amount of lignans absorbed by the body.
Therapeutic Uses
A number of preliminary human and animal studies suggest that lignans may be helpful for cancer prevention , particularly of breast and colon cancer, as well reduction of cholesterol. Other highly preliminary research suggests that flaxseeds or lignans may decrease menopausal symptoms 16 and improve kidney function in various types of kidney disease (specifically, lupus nephritis and polycystic kidney disease).17,18
Warning: Flaxseed or other treatments for kidney disease should be taken only under a doctor's supervision, due to the serious nature of these disorders.
Despite positive preliminary results in animal studies,14,15 studies in humans have yielded mixed results for improving cholesterol levels.45,46
What Is the Scientific Evidence for Lignans?
The most promising use for lignans is in cancer prevention. According to observational studies, people who eat more lignan-containing foods have a lower incidence of breast and perhaps colon cancer.19 This, however, does not prove that lignans are the cause of the benefit, for other factors in these foods, or in the characteristics of the people who consume these foods, may have been responsible. Double-blind, placebo-controlled studies are necessary to prove that a medical treatment provides benefits, and none have yet been reported for lignans. (For information on why this type of study is so important, see Why Does This Database Rely on Double-blind Studies?)
Nonetheless, animal studies offer additional support for a potential cancer-preventive or even cancer-treatment effect. Several studies showed that lignan-rich foods or lignans found in flax inhibited breast and colon cancer in animals 20,21,22 and reduced metastases from melanoma (a type of skin cancer) in mice.23 Test tube studies have found that flaxseed or one of its lignans inhibited the growth of human breast cancer cells 24 and that the lignans enterolactone and enterodiol inhibited the growth of human colon tumor cells.25
In many of these studies, it isn't clear whether lignans are responsible for the benefit seen, as flaxseeds contain many other substances. Animal and human studies have begun to examine specific lignans, and results seem to confirm that at least some of the positive effects probably come from the lignans themselves;26,27,28 still, until more and better designed trials are done, we will not know lignans' precise effects on the human body, or the precise dose needed to prevent cancer.
Safety Issues
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid high intake of flaxseed or purified lignans. One study found that pregnant rats who ate large amounts of flaxseed (5% or 10% of their diet), or a purified lignan present in flaxseed, gave birth to offspring with altered reproductive organs and functions, and that lignans were also transferred to the baby rats during nursing.36 In humans, eating 25 g of flaxseed per day amounts to about 5% of the diet.37
High intake of lignans may not be safe for women with a history of estrogen-sensitive cancer, such as breast cancer or uterine cancer. A few test tube studies suggest that certain cancer cells can be stimulated by lignans such as those present in flaxseed.38 Other studies found that lignans inhibit cancer cell growth.39 As with estrogen, lignans' positive or negative effects on cancer cells may depend on dose, type of cancer cell, and levels of hormones in the body. If you have a history of cancer, particularly breast cancer, talk with your doctor before consuming large amounts of flaxseeds.
Other potential concerns are discussed in the safety section of the Flaxseed article.