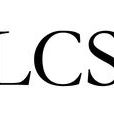LCS是Longest Common Subsequence的縮寫,即最長公共子序列。一個序列,如果是兩個或多個已知序列的子序列,且是所有子序列中最長的,則為最長公共子序列。
比如,對於char x[]="aabcd";有順序且相互相鄰的aabc是其子序列,有順序但是不相鄰的abc也是其公共子序列。即,只要得出序列中各個元素屬於所給出的數列,就是子序列。
再加上char y[]="12abcabcd";對比出才可以得出最長公共子序列abcd。
基本介紹
- 中文名:最長公共子序列
- 外文名:Longest Common Subsequence
- 英文簡稱:LCS
- 學科:計算機
解決方法
算法
代碼實現
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | constmaxlen=200; var i,j:longint; c:array[0..maxlen,0..maxlen]ofbyte; x,y,z:string;{z為x,y的最長公共子序列} begin readln(x); readln(y); fillchar(c,sizeof(c),0); fori:=1tolength(x)do forj:=1tolength(y)do ifx[i]=y[j]thenc[i,j]:=c[i-1,j-1]+1 elseifc[i-1,j]>c[i,j-1]thenc[i,j]:=c[i-1,j] elsec[i,j]:=c[i,j-1]; z:=''; i:=length(x); j:=length(y); writeln(c[i,j]); while(i>0)and(j>0)do ifx[i]=y[j] thenbeginz:=x[i]+z;i:=i-1;j:=j-1end elseifc[i-1,j]>c[i,j-1]theni:=i-1 elsej:=j-1; ifz<>''thenwriteln(z); fori:=1tolength(x)do begin forj:=1tolength(y)dowrite(c[i][j]:3); writeln; end; readln; end. |
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>int main(){ char x[]="aabcdababce"; char y[]="12abcabcdace"; int m=strlen(x); int n=strlen(y); int i,j,k,l; int maxlength=0; int start=0; int count=0;//用來判斷是否匹配的變數 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) //匹配長度的循環 for(j=0; j<n-i+1; j++) //y的起始位置的循環 for(k=0; k<m-i+1; k++) //x的起始位置的循環 { count=0; for(l=0; l<i; l++) //判斷是否匹配,代碼可以最佳化 if(y[j+l]==x[k+l]) count++; if(count==i&&i>maxlength) { maxlength=i;//記錄最大長度 start=j;//記錄最大長度的起起位置 } } if(maxlength==0) printf("NoAnswer"); else for(i=0; i<maxlength; i++) printf("%c",y[start+i]);}#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>int b[50][50];int c[50][50];void lcs(char *x,int m,char *y,int n){ int i; int j; for(i=1; i<=m; i++) c[i][0]=0; for(i=1; i<=n; i++) c[0][i]=0; c[0][0]=0; for(i=1; i<=m; i++) for(j=1; j<=n; j++) { if(x[i-1]==y[j-1]) { c[i][j]=c[i-1][j-1]+1; b[i][j]=1; } else if(c[i-1][j]>c[i][j-1]) { c[i][j]=c[i-1][j]; b[i][j]=2; } else { c[i][j]=c[i][j-1]; b[i][j]=3; } }}void show(int i,int j,char*x){ if(i==0||j==0) return; if(b[i][j]==1) { show(i-1,j-1,x); printf("%c",x[i-1]); } else if(b[i][j]==2) show(i-1,j,x); else show(i,j-1,x);}int main(){ char x[]="aabcdababce"; char y[]="12abcabcdace"; int m=strlen(x); int n=strlen(y); lcs(x,m,y,n); show(m,n,x);}*************************************************************************************************方案3:#include<stdio.h>#include<iostream>#include<string>#include<vector>#include<algorithm>using namespace std;void LCS(const char *str1, const char *str2, string & str){ int size1 = (int)strlen(str1); int size2 = (int)strlen(str2); const char *s1 = str1 - 1; const char *s2 = str2 - 1; vector<vector<int> > chess(size1 + 1, vector<int>(size2 + 2)); int i, j; for (i = 0; i < size1; i++) { chess[i][0] = 0; } for (j = 0; j < size1; j++) { chess[0][j] = 0; } for (i = 1; i < size1; i++) { for (j = 1; j < size2; j++) { if (s1[i] == s2[j])//i j 相等 chess[i][j] = chess[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else { chess[i][j] = max(chess[i][j - 1], chess[i - 1][j]); } } } i = size1; j = size2; while (i != 0 && j != 0) { if (s1[i] == s2[j]) { str.push_back(s1[i]); i--; j--; } else { if (chess[i][j - 1] > chess[i - 1][j]) { j--; } else { i--; } } } reverse(str.begin(), str.end());}int main(){ const char *st1 = "TGGGATCGACTT"; const char *st2 = "AGCCTACGTA"; string str; LCS(st1, st2, str); return 0;}